Orange hawkweed (Hieracium aurantiacum) also known as devil’s paintbrush is a low-growing plant with shallow fibrous roots. The flowering stem is usually leafless. Each bright orange flower is between ½ to 1 inch wide and is grouped in clusters of 2-25 at the top of a small stem. It is a native to Europe and was first discovered in the US in 1945. Information for orange hawkweed was adapted from the Colorado Weed Management Association’s web site.

Figure 1. Orange hawkweed flower. Photograph: UAF Cooperative Extension Archive, University of Alaska – Fairbanks, Bugwood.org

Figure 2. Orange hawkweed plant. Photographer Washington State University Archive, Washington State University, Bugwood.org

Figure 3. Orange hawkweed flower. Photographer: Michael Shephard, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
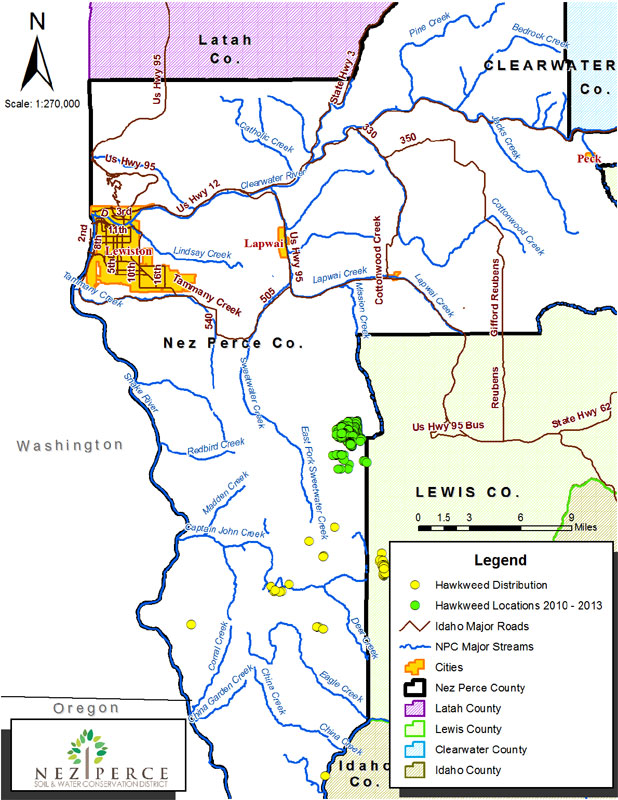
Nez Perce County Distribution:
Orange hawkweed is prevalent in the Craig Mountain area of Nez Perce County. It is prevalent within meadows, grasslands, pastures, and hayfields. The plant forms a large mat, which prevents other vegetation from growing.
Nationwide, USDA reports the weed in thirty-three states.
Figure 4. Orange hawkweed Distribution in Nez Perce County.
Impacts:
- Infests hay fields.
- Animals will not feed.
- Forms mats that prevent other plants from growing.
Biology:
- Likes moist, shady, and grassy areas.
- Seeds remain viable in soil for up to 7 years. (USDA Forest Service)
Control:
Controls include herbicides. The goal is eradication. Contact your local herbicide professional for chemical recommendations.
References:
- FEIS - Fire Effects Information System [Online] (1996, September). Prescribed Fire and Fire Effects Research Work Unit, Rocky Mountain Research Station (producer), US Forest Service. Available: Fire Effects Information [1998, March 12]
- Callihan, R.H., L.M. Wilson, J.P. McCaffery, T.W. Miller, 1997. Hawkweeds. Pacific Northwest Extension Publication 499. Cooperatively published by the University of Idaho Cooperative Extension, Oregon State Cooperative Extension Service, Washington State Cooperative Extension and the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
- Hoffman, R. & K. Kearns, Eds.. 1997. Wisconsin Manual of Control Recommendations for Ecologically Invasive Plants. Wisconsin Dept. Natural Resources. Madison, Wisconsin.. 102pp.
- Whitson, T.D. (Ed.) et al. 1996. Weeds of the West. Western Society of Weed Science in cooperation with Cooperative Extension Services, University of Wyoming. Laramie, Wyoming. 630pp.
- USDA Forest Service, Forest Health Staff, Newton Square, PA. Weed of the Week: Orange Hawkweed. 18 December 2005. 21 August 2013.