Field Bindweed
(Convolvulus arvensis) is a perennial vine native to Eurasia. It was first noted in Virginia in 1739. For more information on this invasive species go to
Invasive Species of Idaho.

Figure 1. Field Bindweed plant. Photograph: Steve Dewey, Utah State University, Bugwood.org

Figure 2. Field bindweed flower. Photograph: Mary Ellen (Mel) Harte, PSES, Bugwood.org

Figure 3. Figure 3. Field bindweed seeds. Photographer Steve Hurste, USDA NRCS PLANTS Database, Bugwood.org.
Nez Perce County Distribution:
Field bindweed is prevalent within Nez Perce County’s agriculture, pastures, gardens, lawns, roadsides, and railways. It is found in dry or moderately moist soils. Nationwide, USDA reports the weed in forty-nine states.
Figure 4. Field bindweed distribution in Nez Perce County. Blue dots show reported distribution areas.
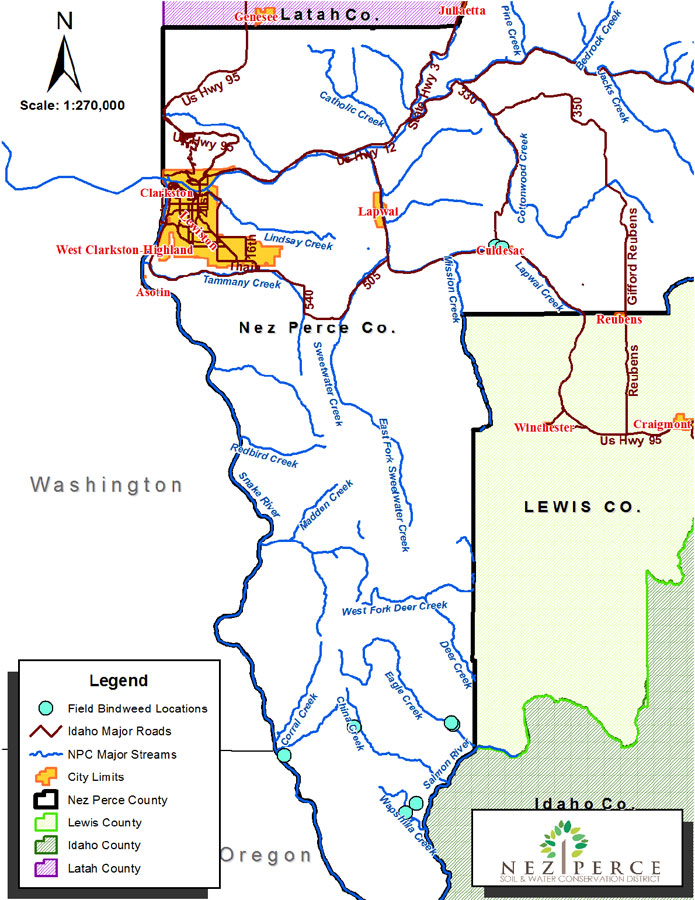
Impacts:
- Heavy grazing on dense populations of field bindweed may have adverse effects on cattle, goats, sheep and hogs. (Morishita)
- Seed can last in soil for up to 60 years. (S. D. Wright, C. L. Elmore and and D. W. Cudney)
Biology:
- Field bindweed flowers persist only 1 day and are insect pollinated. (FIES)
- Seed production by field bindweed is variable and dependent upon environmental conditions.
- In the Pacific Northwest, flowering occurs from mid-spring to late-fall. (FIES)
CONTROL
Controls include herbicides and bio-control agents. Herbicide applications are very expensive and often difficult to apply in steep terrain. Biocontrol agents are a low-cost long-term alternative.
References:
- Zouhar, Kris. 2004. Convolvulus arvensis. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/ [2013, August 20].
- Morishita, Don W., Callihan, Robert H., Eberlein, Charlotte V, McCaffrey, Joseph P., Thill, Donn C. "Field Bindweed." October 2005. http://www.cals.uidaho.edu/edComm/pdf/pnw/pnw0580.pdf. 20 August 2013.
- S. D. Wright, UC Cooperative Extension, Tulare/Kings Co., Plant Sciences emeritus, UC Davis C. L. Elmore and Botany and Plant Sciences emeritus, UC Riverside and D. W. Cudney. How to Manage Pests: Field Bindweed. October 2011. http://www.ipm.ucdavis.edu/PMG/PESTNO